Verifying compatibility: RHISEA (R) vs FORTRAN HISEA
Sosthene Akia
Fisheries and Oceans Canadasosthene.akia@dfo-mpo.ca
Alex Hanke
Fisheries and Oceans Canadaalex.hanke@dfo-mpo.ca
2025-08-19
Source:vignettes/RHISEA_vs_Fortran.Rmd
RHISEA_vs_Fortran.RmdIntroduction
This vignette demonstrates a full workflow to:
- Load baseline and mixture data from package
inst/extdata/ - Simulate multiple datasets mimicking mixed-stock fishery data
- Run HISEA estimators in R (
run_hisea_allwith LDA and LDA_MASS methods) - Run the Fortran executable (assumed available as
hisea.exe) for comparison - Aggregate and visualize estimator results (R vs Fortran)
- Export results to Excel
- Perform simple diagnostics to detect large discrepancies between methods
1. Load baseline and mixture data from installed package
We store data in inst/extdata/ to ensure users can
reproduce the analysis after installation.
baseline_file <- system.file("extdata", "baseline.rda", package = "RHISEA")
mixture_file <- system.file("extdata", "mixture.rda", package = "RHISEA")
load(baseline_file) # loads `baseline` data.frame
load(mixture_file) # loads `mixture` data.frame
# Convert baseline and mixture into HISEA file formats (.std and .mix)
write_std_from_dataframe(df=baseline, stock_col = "population", var_cols = c("d13c", "d18o"))
write_mix_from_dataframe(df=mixture, var_cols = c("d13c_ukn", "d18o_ukn"))2. Define global parameters for simulation and analysis
np <- 2 # Number of populations (stocks)
nv <- 2 # Number of isotopic variables
Nsamps <- 1000 # Number of baseline resamples per simulation
Nmix <- 100 # Number of mixture individuals per simulation
stock_labels <- c("East", "West")
resample_baseline <- FALSE
resampled_baseline_sizes <- c(50, 50)
baseline_std_file <- "hisea.std"
mixture_mix_file <- "hisea.mix"3. Utility functions for reading/writing HISEA files and Fortran outputs
# Read baseline and mixture files, split by stocks
read_base_std_mix <- function(std_path, mix_path) {
std_lines <- readLines(std_path)
mix_lines <- readLines(mix_path)
split_index <- which(grepl("NEXT STOCK", std_lines, ignore.case = TRUE))
end_std <- which(grepl("End of baseline data", std_lines, ignore.case = TRUE))
stock1_base <- std_lines[1:(split_index - 1)]
stock2_base <- std_lines[(split_index + 1):(end_std - 1)]
end_mix <- which(grepl("End of mixed sample", mix_lines, ignore.case = TRUE))
mix_base <- mix_lines[1:(end_mix - 1)]
list(stock1 = stock1_base, stock2 = stock2_base, mix = mix_base)
}
# Write baseline (.std) file from list of matrices
write_std <- function(filepath, stock_list) {
con <- file(filepath, "w")
for (i in seq_along(stock_list)) {
apply(stock_list[[i]], 1, function(row) writeLines(paste(row, collapse = " "), con))
if (i < length(stock_list)) writeLines("NEXT STOCK", con)
}
writeLines("End of baseline data", con)
writeLines("End of file", con)
close(con)
}
# Write mixture (.mix) file from matrix
write_mix <- function(filepath, data) {
con <- file(filepath, "w")
apply(data, 1, function(row) writeLines(paste(row, collapse = " "), con))
writeLines("End of mixed sample", con)
writeLines("End of file", con)
close(con)
}
# Read estimator results from Fortran output files, returns numeric vector of length 2 or NA
read_fort_estimator <- function(file_path) {
if (!file.exists(file_path)) return(c(NA, NA))
line <- readLines(file_path, warn = FALSE)[1]
vals <- as.numeric(unlist(strsplit(trimws(line), "\\s+")))
if (length(vals) == 2) return(vals) else return(c(NA, NA))
}
# Generate Poisson distributed baseline stock data for simulation
generate_stock_data <- function(n, n_vars, base_lambda_val) {
if (base_lambda_val <= 0) base_lambda_val <- 0.1
matrix(rpois(n * n_vars, lambda = base_lambda_val), ncol = n_vars)
}4. Simulation setup and results containers
We simulate 50 datasets, run R estimators and Fortran executable, then store results.
# For reproducible parallel RNG streams
RNGkind("L'Ecuyer-CMRG")
set.seed(42)
n_sim <- 50
results <- list() # R LDA results
results2 <- list() # R LDA_MASS results
est_wide_comparisons <- vector("list", 5) # 5 estimators to compare
est_long_comparisons <- vector("list", 5)
for (j in 1:5) {
est_wide_comparisons[[j]] <- data.frame()
est_long_comparisons[[j]] <- data.frame()
}
# Precompute RNG streams for independent simulations
streams <- vector("list", n_sim)
streams[[1]] <- .Random.seed
for (i in 2:n_sim) {
streams[[i]] <- parallel::nextRNGStream(streams[[i - 1]])
}5. Main simulation loop
for (i in 1:n_sim) {
cat("\n--- Simulation ", i, " ---\n")
# Activate independent RNG stream for reproducibility
.Random.seed <- streams[[i]]
# Simulate baseline stock data with slightly different lambda values per stock
base_lambda_stock1 <- runif(1, 15, 25)
lambda_shift_stock2 <- runif(1, 5, 15)
stock1_data <- generate_stock_data(100, nv, base_lambda_stock1)
stock2_data <- generate_stock_data(100, nv, base_lambda_stock1 + lambda_shift_stock2)
# Write baseline to .std file
write_std(baseline_std_file, list(stock1_data, stock2_data))
# Generate mixture based on random proportions
current_sim_comp <- as.numeric(gtools::rdirichlet(1, alpha = rep(1, np)))
n_from_stocks <- round(Nmix * current_sim_comp)
if (sum(n_from_stocks) != Nmix) n_from_stocks[1] <- n_from_stocks[1] + (Nmix - sum(n_from_stocks))
mixture_data <- rbind(
stock1_data[sample(nrow(stock1_data), n_from_stocks[1], replace = TRUE), ],
stock2_data[sample(nrow(stock2_data), n_from_stocks[2], replace = TRUE), ]
)
mixture_data <- mixture_data[sample(nrow(mixture_data)), ]
# Write mixture to .mix file
write_mix(mixture_mix_file, mixture_data)
# Run Fortran HISEA executable
system("hisea.exe", wait = TRUE)
out_file <- sprintf("hisea%02d.out", i)
if (file.exists("hisea.out")) file.rename("hisea.out", out_file)
# Run R-based estimations with LDA and LDA_MASS
r_result <- run_hisea_all(
type = "ANALYSIS",
np = np,
phi_method = "standard",
nv = nv,
resample_baseline = resample_baseline,
resampled_baseline_sizes = resampled_baseline_sizes,
seed_val = 123456,
nsamps = Nsamps,
Nmix = Nmix,
baseline_input = baseline_std_file,
mix_input = mixture_mix_file,
method_class = "LDA",
stocks_names = stock_labels
)
r_df <- as.data.frame(r_result$mean)
colnames(r_df) <- paste0("Estimator_", 1:5)
r_df$Stock <- stock_labels
r_df$Simulation <- paste0("Sim_", i)
results[[i]] <- r_df
r_result2 <- run_hisea_all(
type = "ANALYSIS",
np = np,
phi_method = "standard",
nv = nv,
resample_baseline = resample_baseline,
resampled_baseline_sizes = resampled_baseline_sizes,
seed_val = 123456,
nsamps = Nsamps,
Nmix = Nmix,
baseline_input = baseline_std_file,
mix_input = mixture_mix_file,
method_class = "LDA_MASS",
stocks_names = stock_labels
)
r_df2 <- as.data.frame(r_result2$mean)
colnames(r_df2) <- paste0("Estimator_", 1:5)
r_df2$Stock <- stock_labels
r_df2$Simulation <- paste0("Sim_", i)
results2[[i]] <- r_df2
# Read Fortran estimators from fort.xx files (10 + estimator index)
fort_estimates <- lapply(1:5, function(j) read_fort_estimator(sprintf("fort.%02d", 10 + j)))
# Store wide and long format comparisons for each estimator
for (j in 1:5) {
wide_df <- data.frame(
Simulation = paste0("Sim_", i),
Stock = stock_labels,
R = r_df[[paste0("Estimator_", j)]],
Mass = r_df2[[paste0("Estimator_", j)]],
Fortran = fort_estimates[[j]]
)
est_wide_comparisons[[j]] <- rbind(est_wide_comparisons[[j]], wide_df)
long_df <- data.frame(
Simulation = rep(paste0("Sim_", i), times = 6),
Estimate = paste0("Estimator_", j),
Stock = rep(stock_labels, times = 3),
Method = rep(c("Fortran", "LDA_R", "LDA_MASS"), each = 2),
Value = c(
fort_estimates[[j]],
r_df[[paste0("Estimator_", j)]],
r_df2[[paste0("Estimator_", j)]]
)
)
est_long_comparisons[[j]] <- rbind(est_long_comparisons[[j]], long_df)
}
}
#>
#> --- Simulation 1 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 2 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 3 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 4 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 5 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 6 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 7 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 8 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 9 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 10 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 11 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 12 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 13 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 14 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 15 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 16 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 17 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 18 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 19 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 20 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 21 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 22 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 23 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 24 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 25 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 26 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 27 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 28 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 29 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 30 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 31 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 32 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 33 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 34 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 35 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 36 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 37 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 38 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 39 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 40 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 41 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 42 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 43 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 44 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 45 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 46 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 47 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 48 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 49 ---
#>
#> --- Simulation 50 ---6. Aggregate and summarize results
final_results <- do.call(rbind, results)
# Round values and compute residuals between R and Fortran
for (j in 1:5) {
est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$R <- round(est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$R, 4)
est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$Mass <- round(est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$Mass, 4)
est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$res <- est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$R - est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$Fortran
est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$res_mass <- est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$Mass - est_wide_comparisons[[j]]$Fortran
}7. Export results to Excel
write_xlsx(list(
R_Only_Results = final_results,
Estimator1_Comparison = est_wide_comparisons[[1]],
Estimator2_Comparison = est_wide_comparisons[[2]],
Estimator3_Comparison = est_wide_comparisons[[3]],
Estimator4_Comparison = est_wide_comparisons[[4]],
Estimator5_Comparison = est_wide_comparisons[[5]]
), path = "hisea_r_vs_fortran_results.xlsx")
cat("\nResults saved to hisea_r_vs_fortran_results.xlsx\n")
#>
#> Results saved to hisea_r_vs_fortran_results.xlsx8. Visualization: Compare R vs Fortran estimators
plot_estimator <- function(df, est_label) {
ggplot(df, aes(x = R, y = Fortran, color = Stock)) +
geom_point(size = 2) +
facet_wrap(~Stock) +
geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0, linetype = "dashed", color = "gray40") +
labs(
title = paste("Comparison of", est_label),
subtitle = "R vs Fortran (simulated baseline & mixture)",
x = paste(est_label, "(R)"),
y = paste(est_label, "(Fortran)")
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 13)
}
for (j in 1:5) {
print(plot_estimator(est_wide_comparisons[[j]], paste0("Estimator ", j)))
}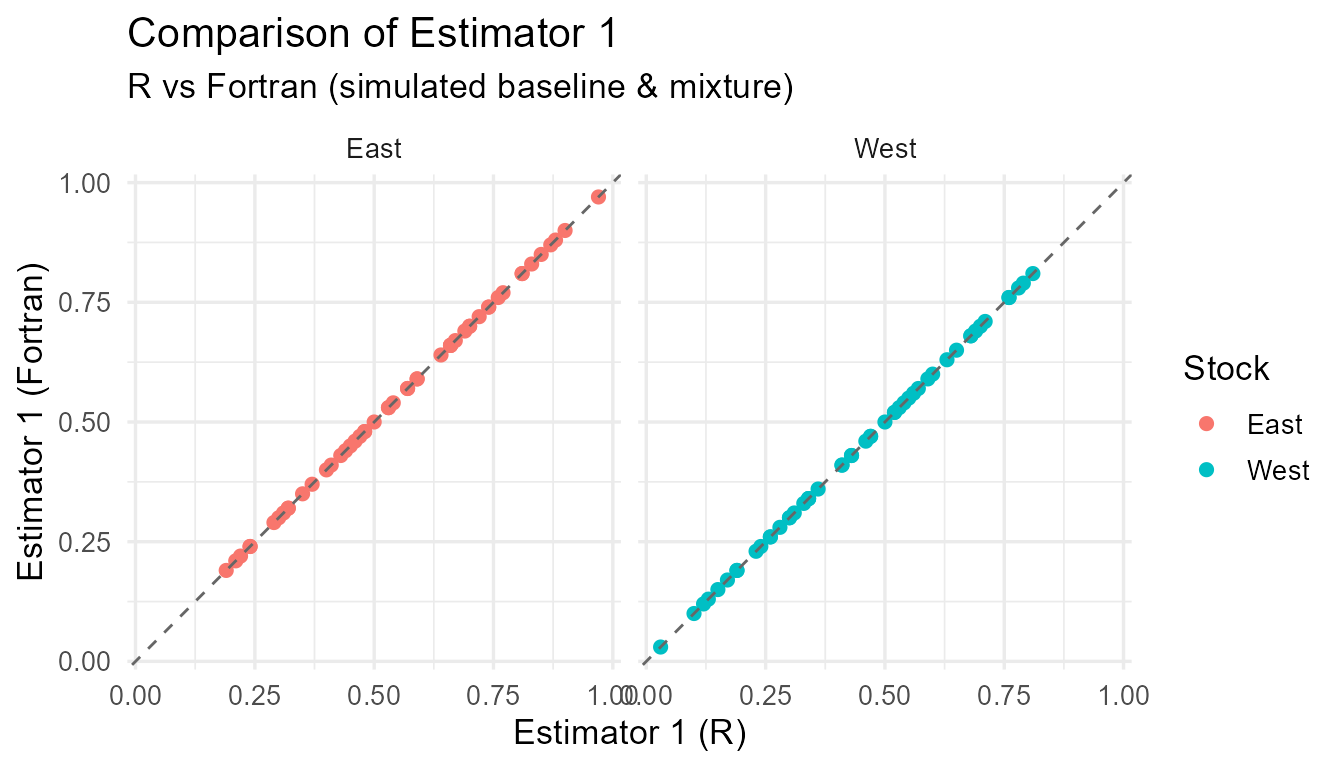
Comparison of R vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
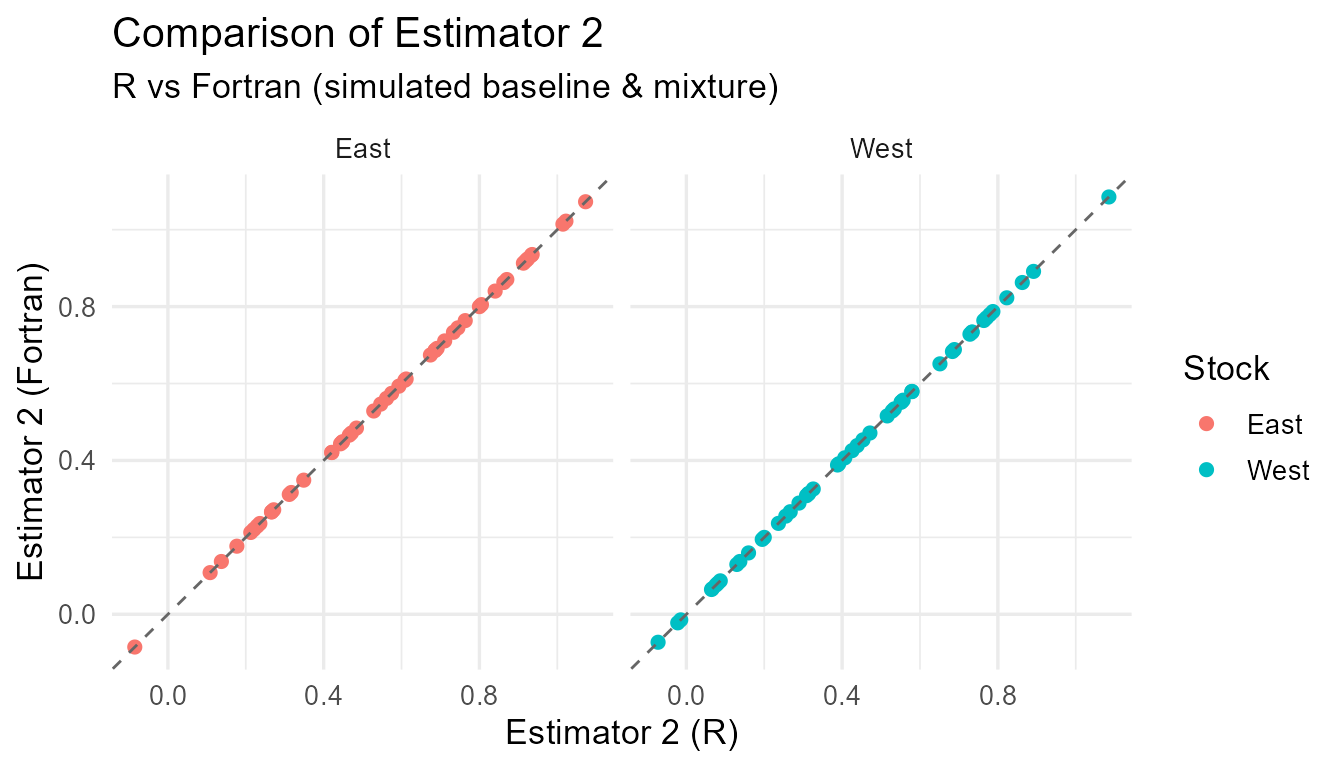
Comparison of R vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
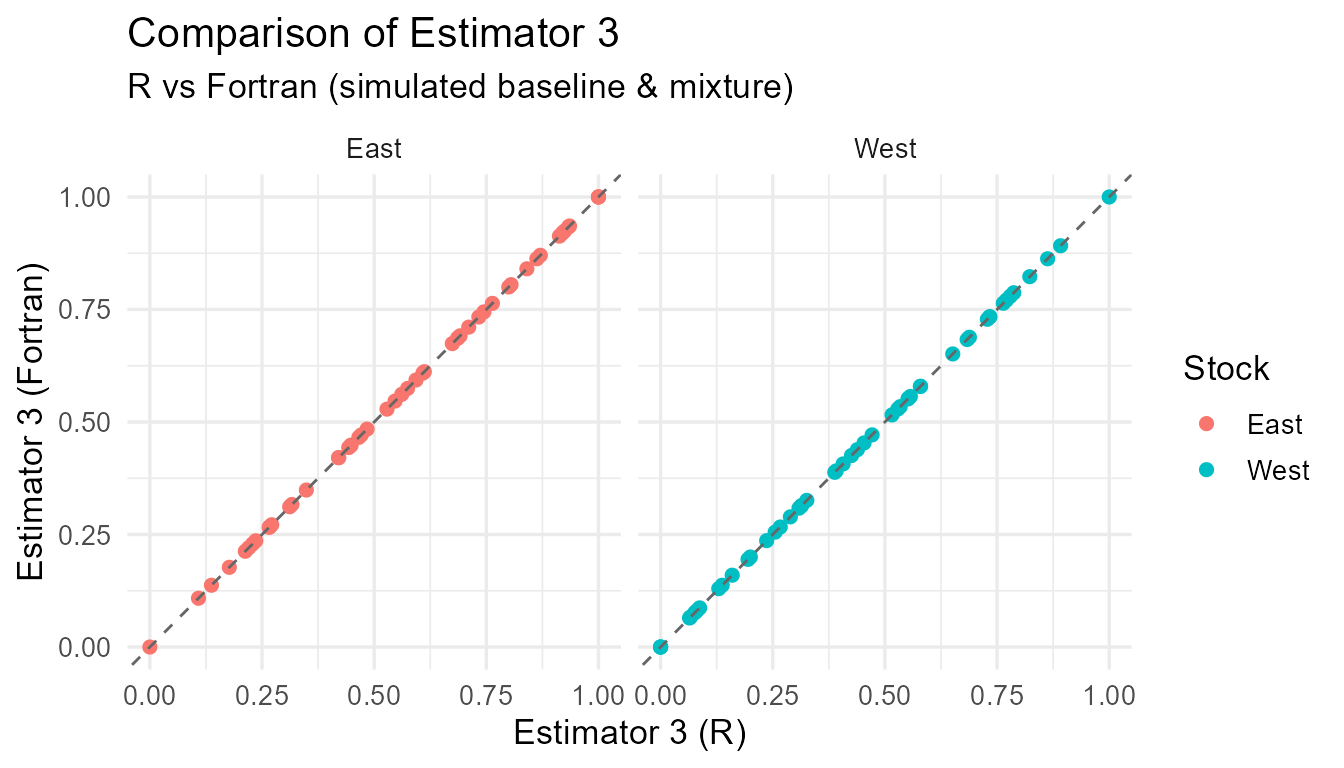
Comparison of R vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
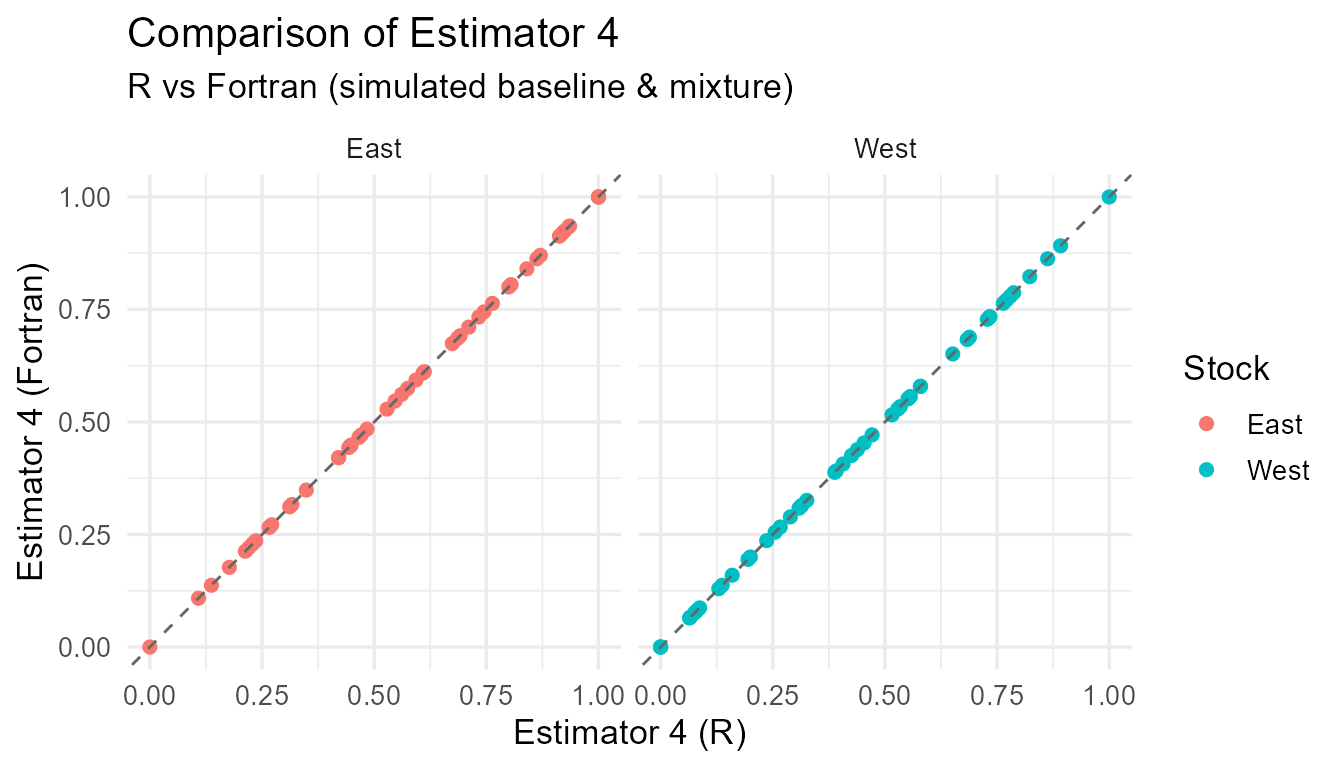
Comparison of R vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
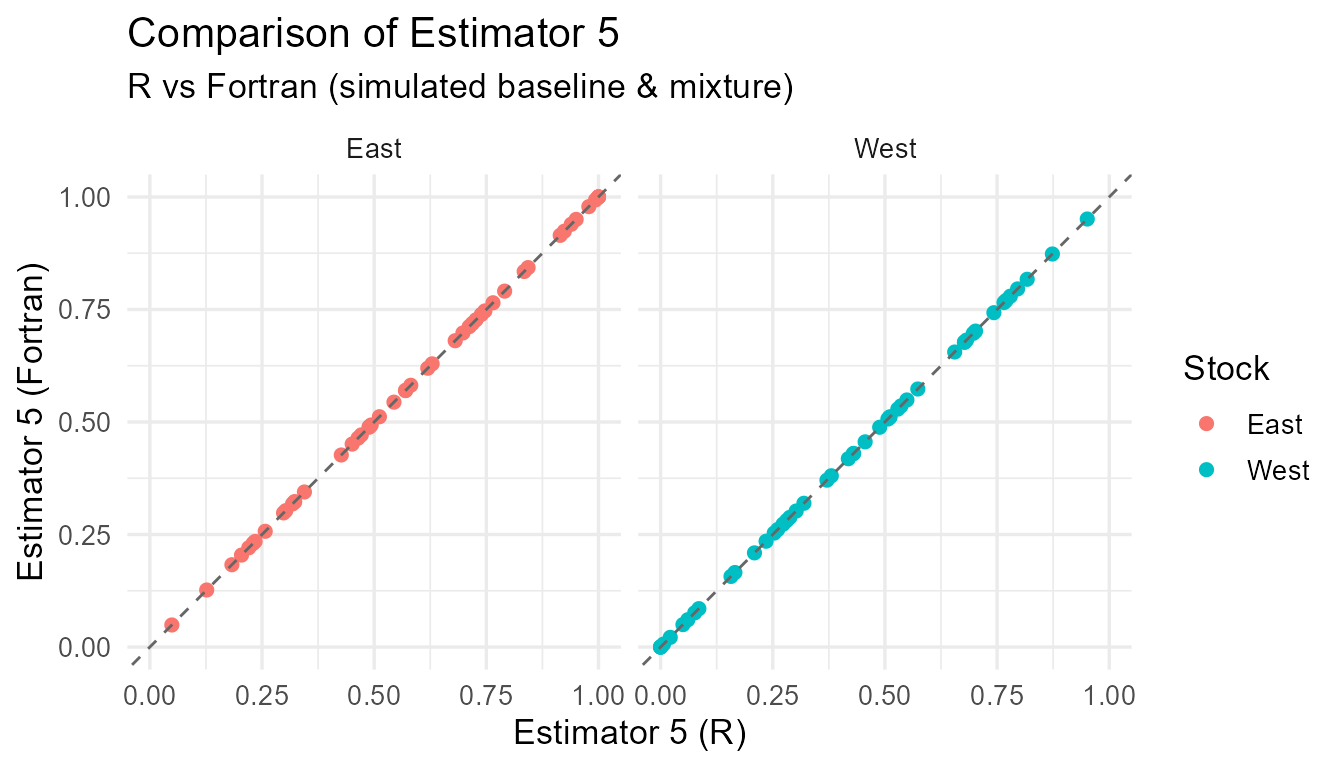
Comparison of R vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
9. Visualization: Compare R_MASS vs Fortran estimators
plot_estimator2 <- function(df, est_label) {
ggplot(df, aes(x = Mass, y = Fortran, color = Stock)) +
geom_point(size = 2) +
facet_wrap(~Stock) +
geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0, linetype = "dashed", color = "gray40") +
labs(
title = paste("Comparison of", est_label),
subtitle = "R_MASS vs Fortran (simulated baseline & mixture)",
x = paste(est_label, "(R_MASS)"),
y = paste(est_label, "(Fortran)")
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 13)
}
for (j in 1:5) {
print(plot_estimator2(est_wide_comparisons[[j]], paste0("Estimator ", j)))
}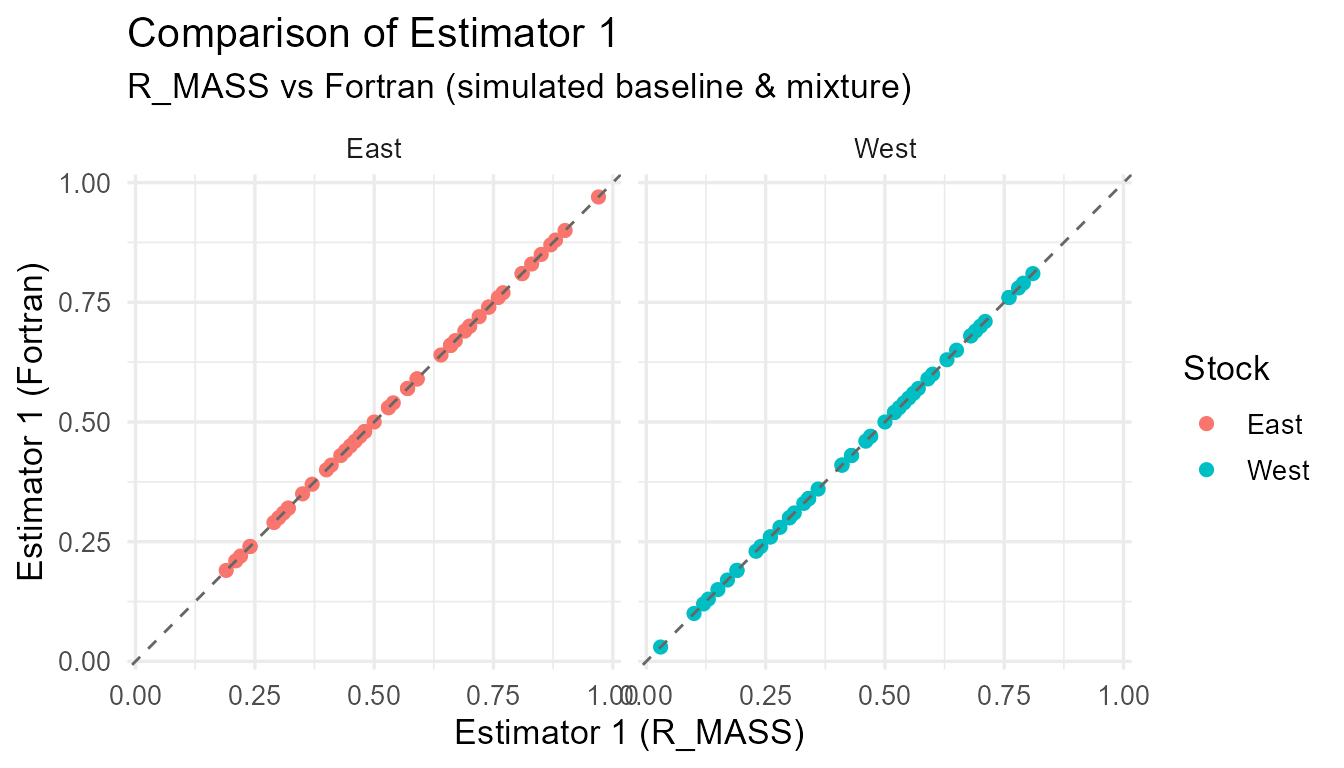
Comparison of R_MASS vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
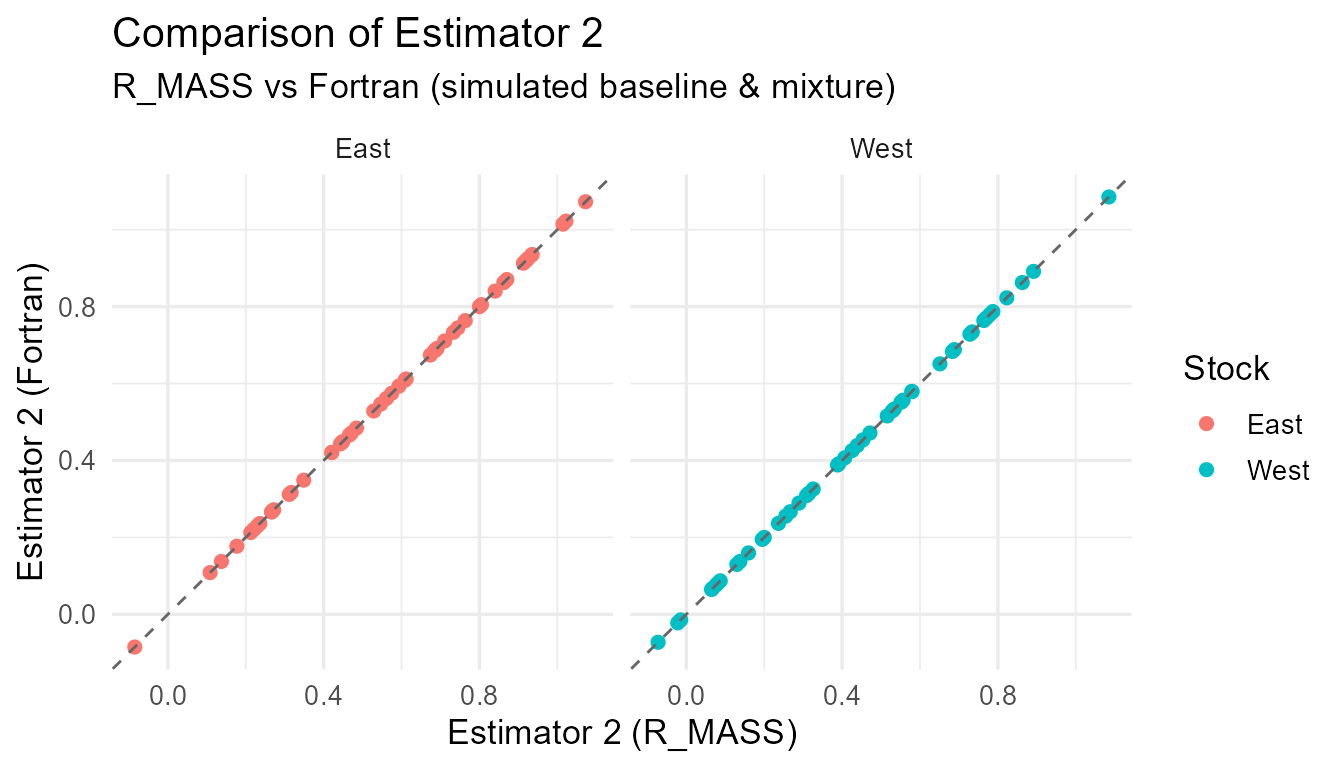
Comparison of R_MASS vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
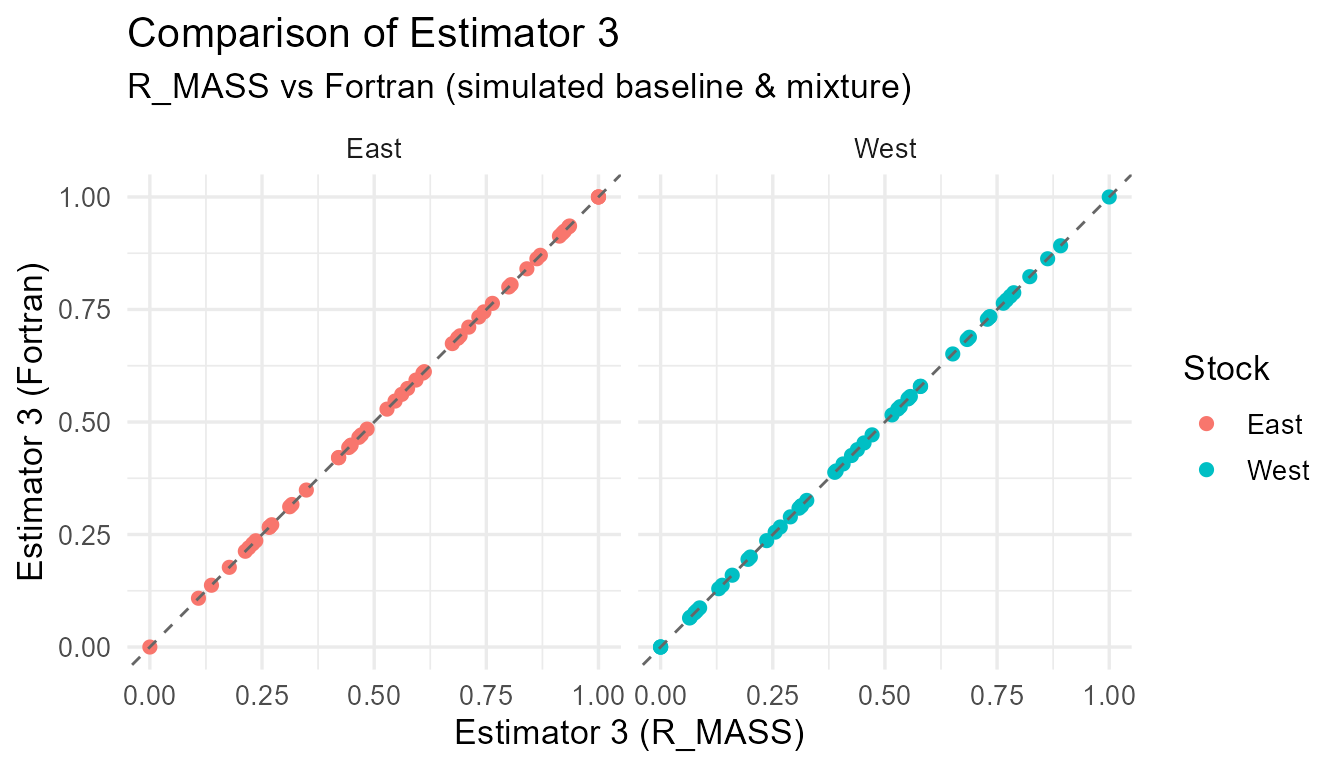
Comparison of R_MASS vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
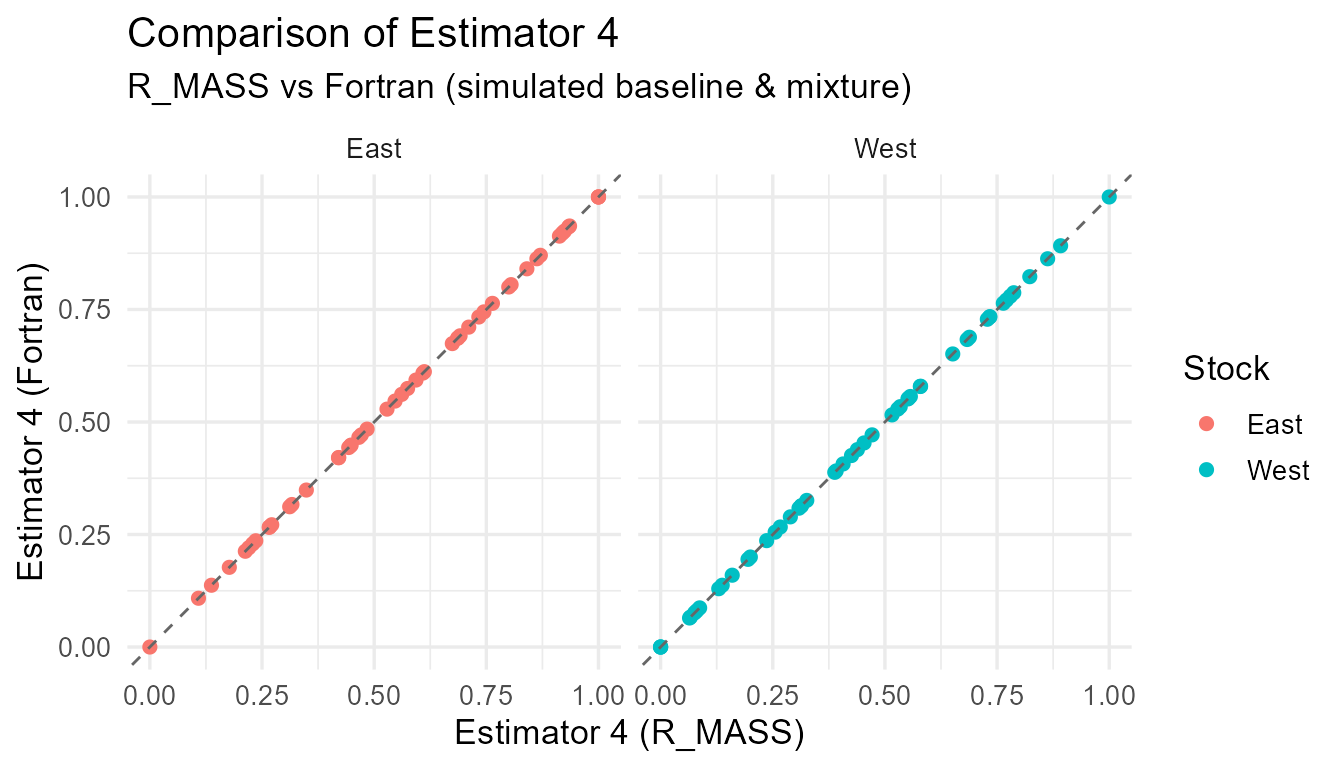
Comparison of R_MASS vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
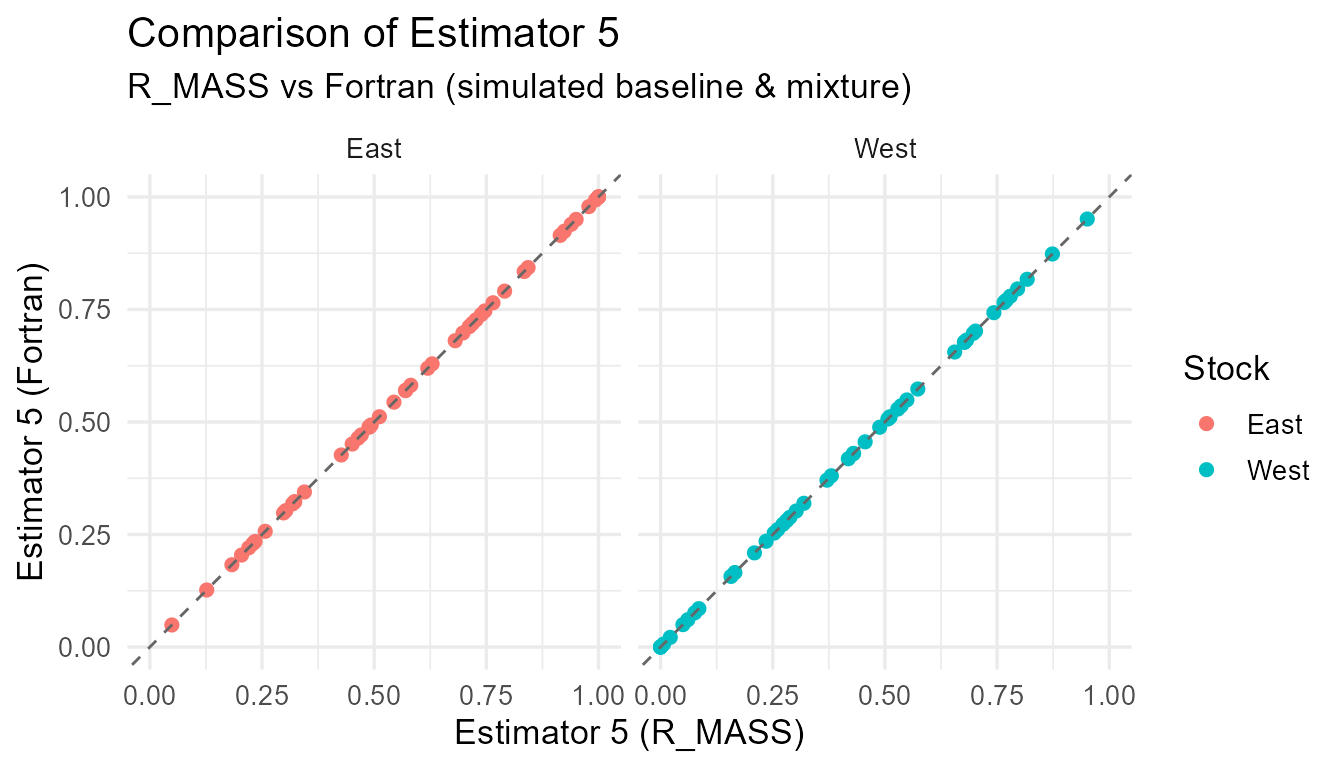
Comparison of R_MASS vs Fortran estimates for each estimator
10. Boxplot for all estimators and methods
all_wide <- do.call(rbind, est_wide_comparisons)
all_long <- do.call(rbind, est_long_comparisons)
ggplot(all_long, aes(x = Method, y = Value, fill = Method)) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = 0.15), outlier.shape = NA) +
stat_summary(
fun = mean,
geom = "point",
shape = 23, size = 3,
fill = "white"
) +
stat_summary(
fun = mean,
geom = "text",
aes(label = sprintf("%.4f", after_stat(y))),
hjust = 1.2,
vjust = 0.1,
size = 3
) +
facet_grid(Estimate ~ Stock) +
theme_minimal() +
labs(
title = "Comparison of Estimation Methods Across Simulations",
y = "Estimated Proportion",
x = "Method"
) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1))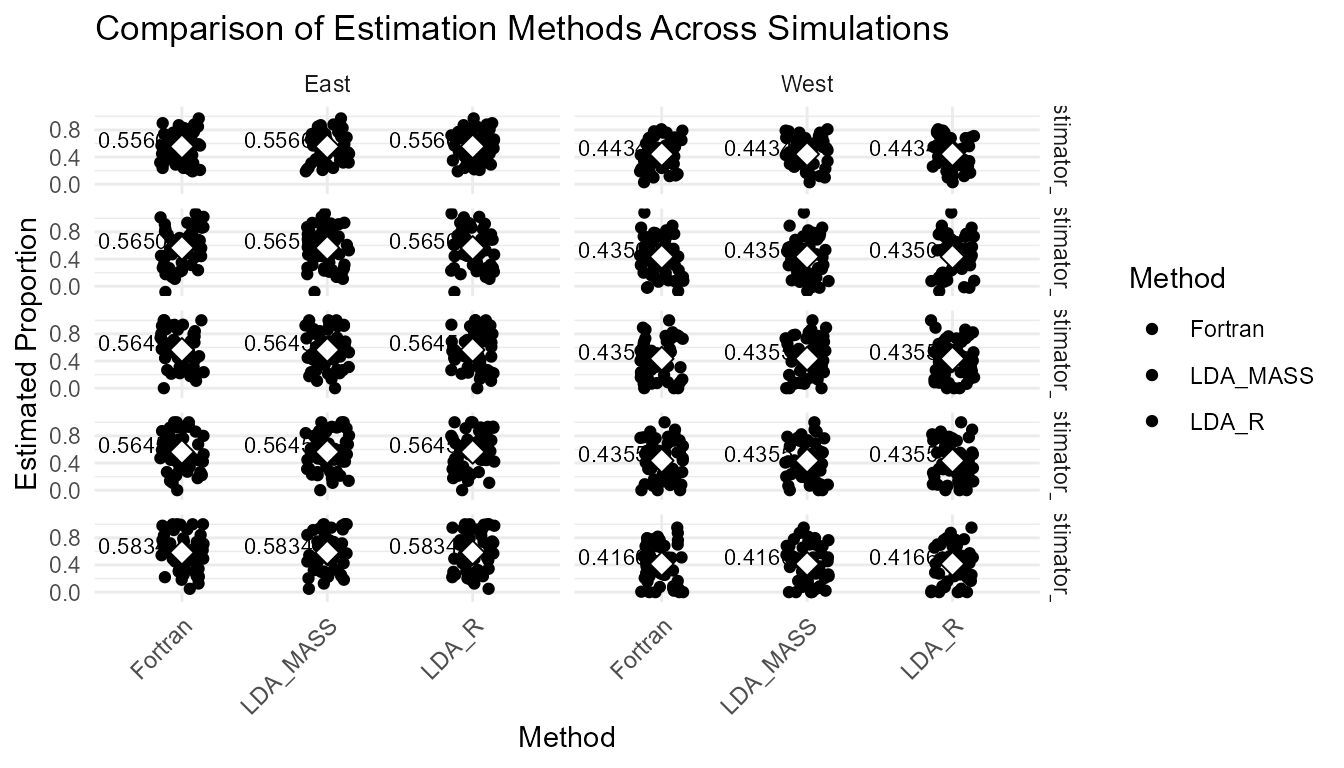
Boxplot comparing all methods across simulations
11. Diagnostics: Alert if large divergence detected
threshold <- 0.05 # 5% difference threshold
max_diffs <- sapply(est_wide_comparisons, function(df) max(abs(df$R - df$Fortran), na.rm = TRUE))
if (any(max_diffs > threshold)) {
warning(
paste(
"Warning: Large divergence detected between R and Fortran estimators.",
"Maximum differences by estimator:",
paste0("Estimator", 1:5, "=", round(max_diffs, 3), collapse = "; ")
)
)
} else {
message("No large divergences detected between R and Fortran estimators.")
}Conclusion
This vignette provides a full workflow to simulate, run, compare and diagnose the HISEA estimation methods in R versus the original Fortran implementation. All results and plots help verify the consistency and quality of the R implementation, and the diagnostics alert when large discrepancies occur.